Aerospike Vector Search Architecture
This page describes three distinct layers and their features in a fully functional Aerospike Vector Search (AVS) platform.
Overview
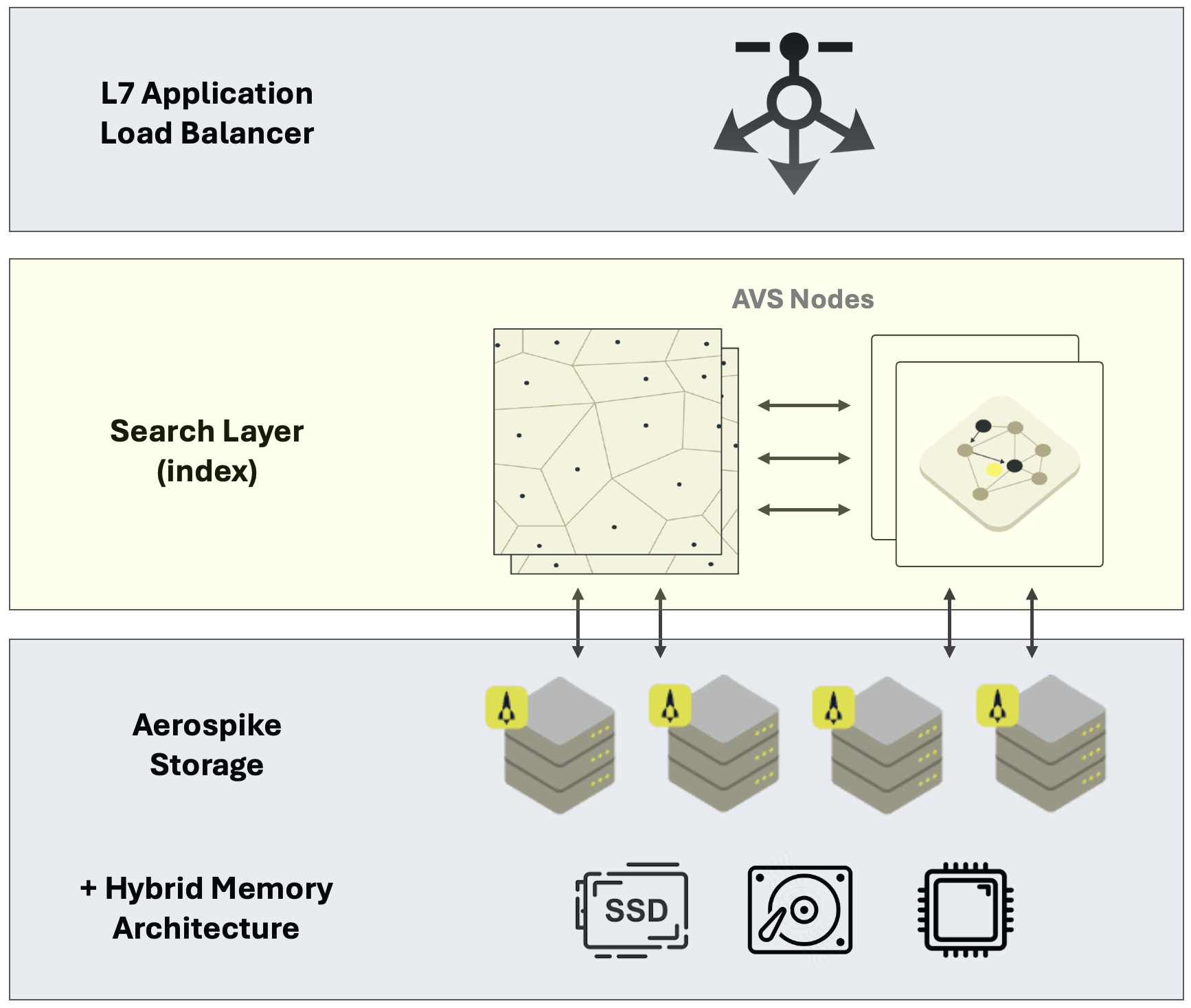
It is important to understand how AVS is structured if you plan to operate AVS yourself. The layers are:
- Storage layer - the Aerospike Database cluster
- Search layer - the AVS cluster
- Application layer - load balancer
Aerospike Database
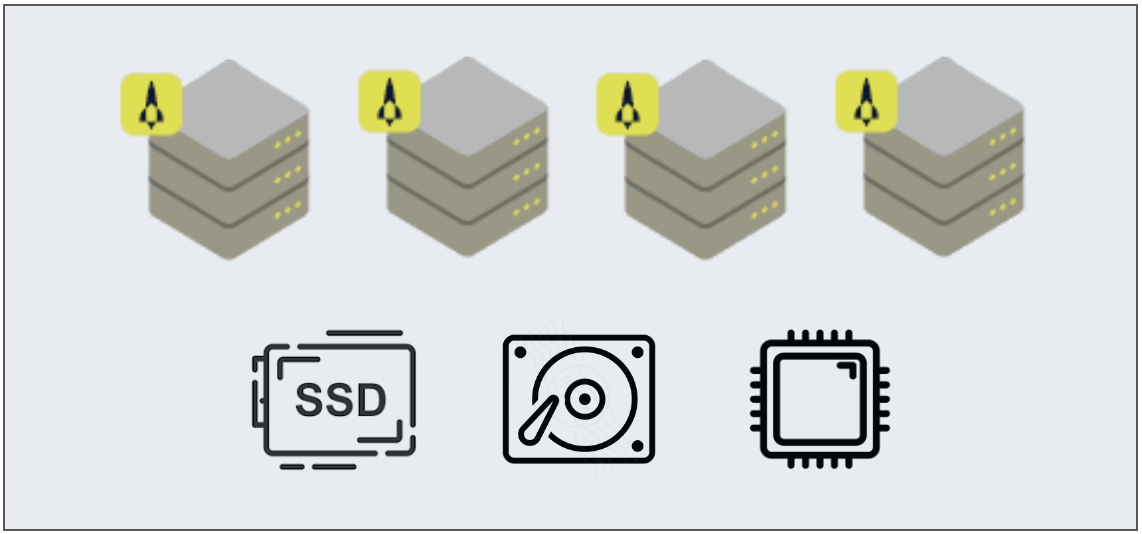
Aerospike Database is built on a horizontally scalable storage system and delivers high performance, low latency, and reliability. Its data partitioning and hybrid memory architecture make it especially well-suited for AVS.
The Aerospike Database storage layer provides the following core pieces of functionality related to AVS:
- Stores state for the AVS system. This is referred to as index metadata and requires a specific namespace configuration in Aerospike Database to start the search layer.
- Stores the vector data and associated metadata for your search application.
- Stores the index data for your Hierarchical Navigable Small World (HNSW) index.
Storage layer features
AVS can use several core storage layer features as described in the following sections:
Hybrid memory architecture
Aerospike Database's hybrid memory architecture takes advantage of an in-memory index with SSD-based data storage. It is important to understand these basics before defining index and data storage.
Native data replication and XDR
Aerospike Database has multiple options for data replication that are relevant to how you store your core AVS search application. Replication features require specification at the namespace level for your index or data when used with AVS.
These replication features are:
- Namespace Durability - Specifies a replication factor for the data in a particular namespace.
- Cross Data Center Replication (XDR) - Replicates an entire namespace to a separate Aerospike cluster.
Backup and restore capabilities
Aerospike Database's backup and restore tools work with vector and index data. For information on how to use Aerospike tools, see the backup and recovery guide.
Encryption and compression features
You can configure TLS for AVS and Aerospike Database to encrypt data at rest and encrypt data in motion. You can also configure compression to optimize storage. Encryption and compression features require specification at the namespace level for your index or data when used with AVS.
AVS cluster
The search layer is a collection of clustered AVS nodes that can be assigned specific roles scaled for specific functionality according to your query and ingest throughput needs. Each node can perform search, ingestion, distributed and standalone indexing, depending on its configured role.
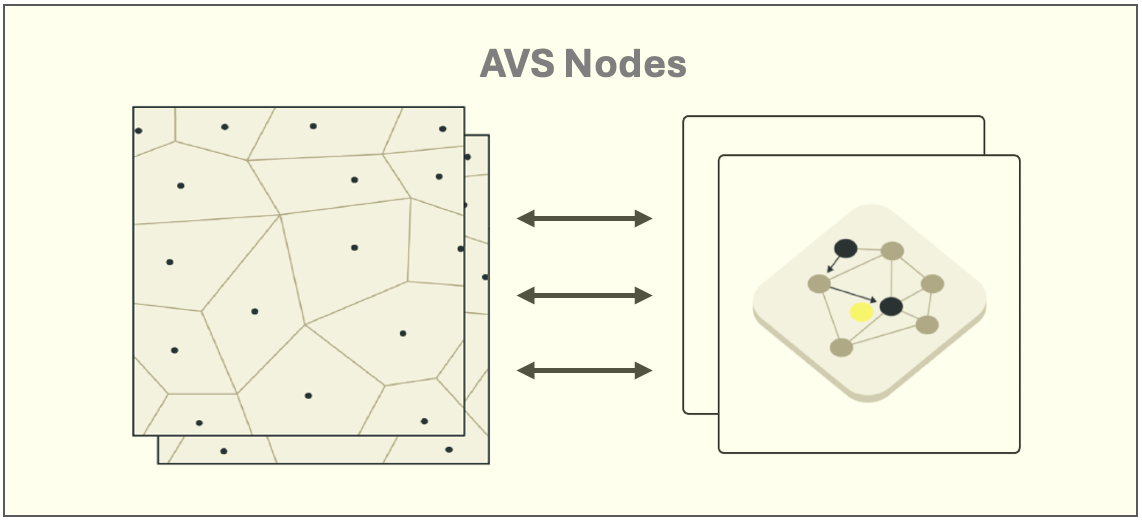
Clustering
AVS uses the same clustering algorithm as Aerospike Database to add nodes to the pool and utilize the resources of those nodes. Clustering happens by default, but you can use several configuration options for heartbeat and interconnect to configure details like encryption and intervals used by the system.
Caching
AVS query nodes cache the index in memory on the AVS nodes. This ensures optimal performance, and that scaling can meet specific performance requirements for throughput and latency. You can configure caching at the index level to set expiration and specifics about including vector records.
For details, visit our caching guide.
Ingestion and indexing
AVS index nodes handle inserts, updates and deletions of your vector data. You can index data in two ways:
- Distributed index updates are designed to be handled across across your entire culture and is ideal for capturing real-time updates.
- Standalone indexing builds your entire index in memory. This is ideal when indexing all of your data in batch.
For details, see ingestion and indexing.
Application load balancer (optional)
If you want to provide AVS as a service from a host URL, you need to configure an application load balancer.
Using without a load balancer (default behavior)
If you are not exposing AVS to the internet, you can allow clients to connect directly to an AVS node and use that connection to discover other nodes in the cluster. You must specify at least one valid node as a seed when creating your cluster and set is_loadbalancer to false.
Using with a load balancer
A layer-7 load-balancer is required to load-balance gRPC connections properly. Layer-7 load balancers can route gRPC calls based on the specific method being invoked, enabling more intelligent traffic management. Additionally, this layer provides TLS termination and retry logic. If you are using a load balancer, ensure that the is_loadbalancer configuration is set to true when creating your client.
A layer-4 load balancer from a cloud provider is not sufficient for AVS because it does not properly load balance the gRPC connection. See the Kubernetes installation guide for details about installing Istio.